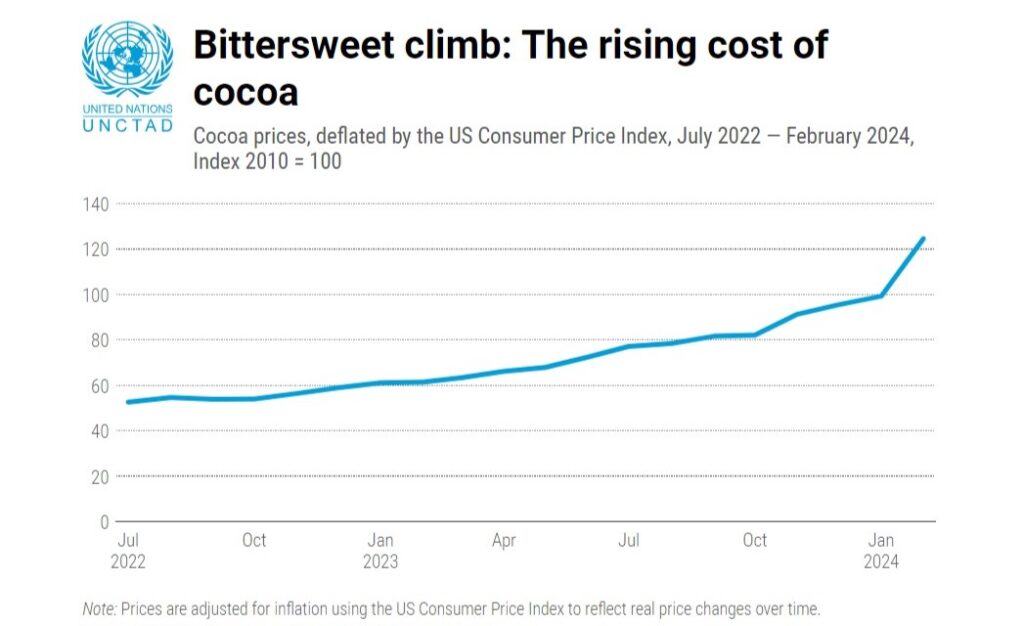
The impact of extreme weather and changing climate patterns on cocoa is becoming increasingly evident, due to number of reasons:
Weather Disruptions: Cocoa-producing regions, particularly in West Africa (e.g., Ivory Coast and Ghana, which account for more than 60% of global cocoa production), have experienced erratic weather patterns. This includes unusual rainfall, prolonged dry spells, and higher temperatures, which can adversely affect cocoa yields.
Crop Diseases: Climate change has also been linked to the increased prevalence of crop diseases and pests. Cocoa trees are susceptible to diseases like Black Pod and pests like the cocoa pod borer. These threats can decimate crops, further reducing yields.
Economic Impact: The shortfall in cocoa harvests for three consecutive years has significant economic implications. Cocoa prices have surged due to the tight supply, impacting the cost of chocolate production. This price increase is often passed on to consumers, leading to higher retail prices for chocolate products.
Sustainability Efforts: In response to these challenges, there are growing efforts to promote sustainable cocoa farming practices. These include the development of climate-resilient cocoa varieties, improved agricultural techniques, and initiatives to support farmers in adapting to changing conditions.
Global Supply Chain: The interconnected nature of the global supply chain means that disruptions in cocoa production can have widespread effects. Chocolate manufacturers may face supply shortages, and smallholder farmers who rely on cocoa as a primary source of income are particularly vulnerable.